# 数据工厂-生成接口通用用例_1
**Repository Path**: rain_yang/datafactory_1
## Basic Information
- **Project Name**: 数据工厂-生成接口通用用例_1
- **Description**: 自动生成接口通用用例。
- **Primary Language**: Java
- **License**: Not specified
- **Default Branch**: master
- **Homepage**: None
- **GVP Project**: No
## Statistics
- **Stars**: 0
- **Forks**: 5
- **Created**: 2023-10-07
- **Last Updated**: 2023-10-07
## Categories & Tags
**Categories**: Uncategorized
**Tags**: None
## README
## 一、背景介绍
> 有哪些用例是可以通用且固定的?
- 针对之前提到的**接口用例设计思路**,拆分为**三个切入点**:
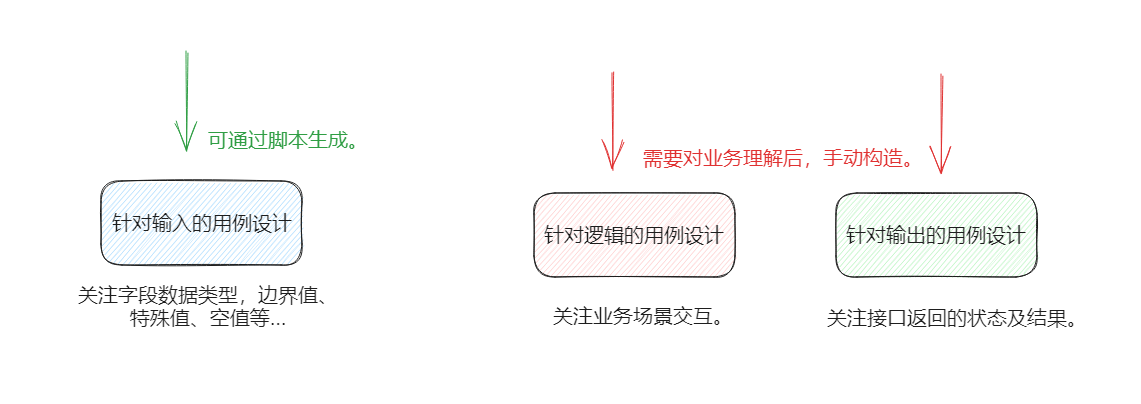
- 举个例子:
```json
{
"field": "value"
}
```
- 针对这个字符串类型的入参我们可以设计:
- 当前数据类型入参(例如:空串,空格字符,特殊字符,字符个数上下限等。)
- 非当前数据类型入参(例如:整型、浮点类型、布尔类型等。)
- 特殊值(0、null值等。)
## 二、前置准备
> 运行数据工厂的前提条件。
- `java` 开发及运行环境。
- `maven` 构建工具。
- 使用到的依赖:
```xml
com.alibaba
fastjson
1.2.76
org.apache.poi
poi
4.1.2
org.apache.poi
poi-ooxml
4.1.2
```
## 三、设计思路
> 工具类之间是如何交互的。
- **包层级目录**:
```tex
+---java
| \---com
| \---example
| \---myproject
| +---boot
| | Launcher.java
| |
| +---core
| | DataFactory.java
| |
| +---pojo
| | WriteBackData.java
| |
| \---util
| CaseUtils.java
| ExcelUtils.java
| FileUtils.java
| JsonPathParser.java
| JsonUtils.java
|
\---resources
request.json
TestCase.xls
```
- **脚本执行的主流程**:
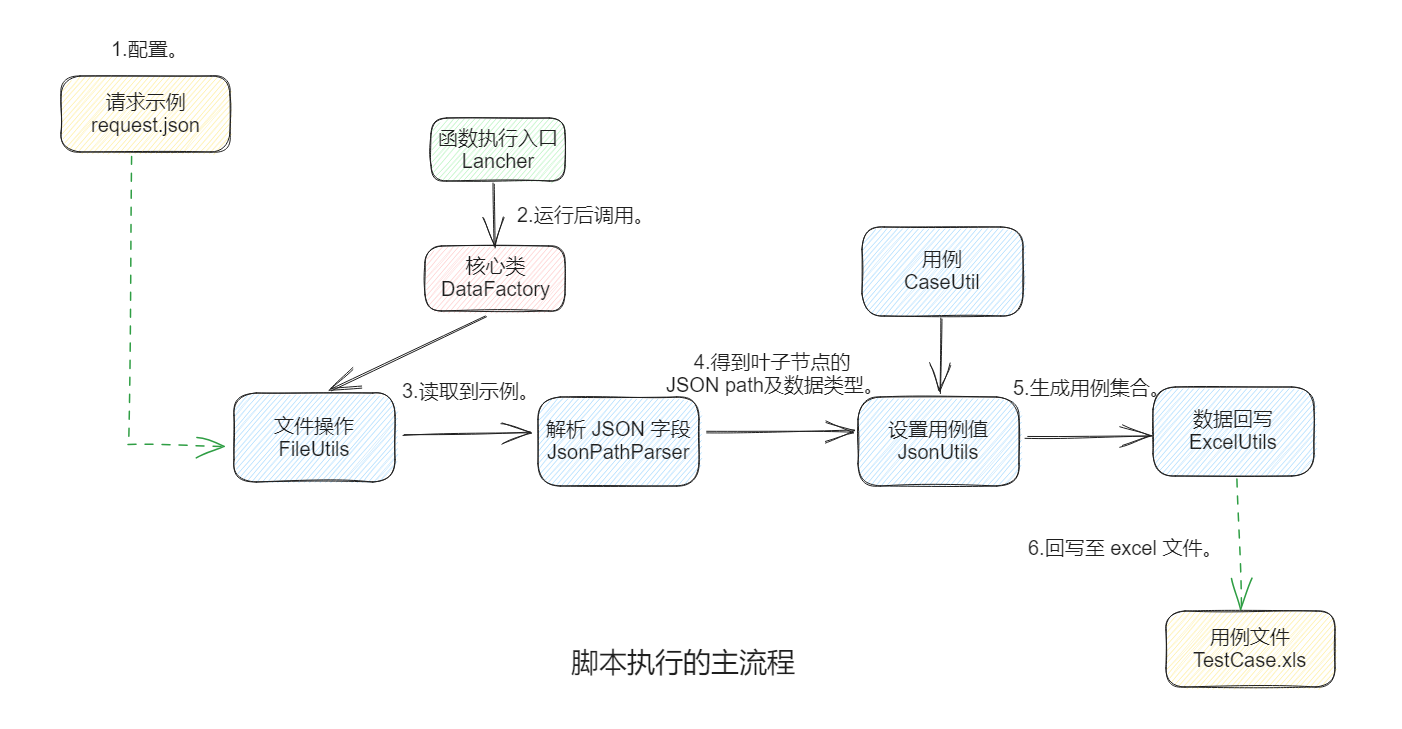
## 四、代码具体实现
- **Launcher**(启动类):
```java
package com.example.myproject.boot;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.example.myproject.core.DataFactory;
/**
* 执行入口。
*
* @author Jan
* @date 2023/08
*/
public class Launcher {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 这里支持传入自定义的用例拓展字段 -> new JSONObject() 。
DataFactory.runAndCreateTestCases(null);
}
}
```
- **DataFactory**(核心类):
```java
package com.example.myproject.core;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONPath;
import com.example.myproject.pojo.WriteBackData;
import com.example.myproject.util.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 数据工厂。
*
* @author Jan
* @date 2023/08
*/
public class DataFactory {
private DataFactory() {
}
/**
* 回写数据的集合。
*/
private static final List WRITE_BACK_DATA = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 运行和创建测试用例。
*
* @param ext ext 额外的拓展参数。
* @throws Exception 异常。
*/
public static void runAndCreateTestCases(JSONObject ext) throws Exception {
// 获取请求示例。
String jsonStr = FileUtils.readSampleRequest();
// 解析json的字段数据类型及jsonPath。
Set jsonPaths = JsonPathParser.getJsonPaths(jsonStr);
for (String jsonPath : jsonPaths) {
// 字段数据类型。
String filedDataType = JSONPath.read(jsonStr, jsonPath).getClass().getSimpleName();
// 跳过复合类型。
if ("JSONObject".equals(filedDataType)) {
continue;
}
// 字段名。
String[] split = jsonPath.split("\\.");
String filedName = split[split.length - 1];
// 通过反射生成对应数据类型的测试用例。
List